Overview of Southeast Asia’s Economy
Southeast Asia is one of the world’s most dynamic and fast-growing regions, comprising 11 countries including Indonesia, Thailand, Singapore, Malaysia, Vietnam, the Philippines, and others. As of 2025, the region’s economy continues to expand rapidly due to strong demographics, increasing foreign investment, industrialization, and growing digital innovation. Understanding Southeast Asia’s economic ranking requires examining the region’s gross domestic product (GDP), growth rates, economic diversification, and regional comparison.business.cornell
GDP Rankings of Southeast Asian Countries
Top Economies by GDP Size
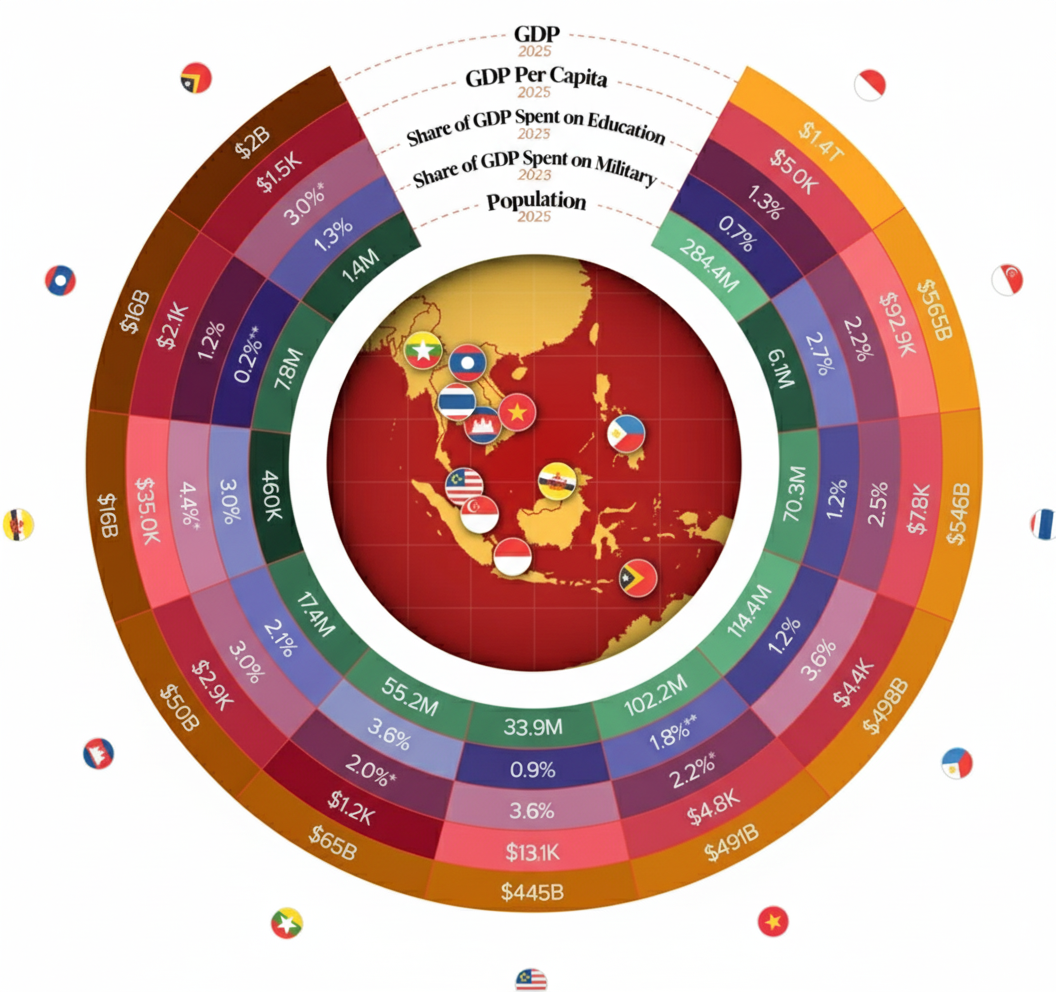
As of 2025, Indonesia holds the position as the largest economy in Southeast Asia by GDP, followed by Thailand, Singapore, and Malaysia. The latest figures show the following rankings based on nominal GDP:
-
Indonesia: The region’s economic powerhouse with a GDP exceeding $1.3 trillion, benefiting from vast natural resources, large domestic consumption, and a growing manufacturing base.
-
Thailand: Southeast Asia’s second-largest economy, with a GDP around $580 billion, driven by tourism, automotive production, and exports.
-
Singapore: Despite its small size, Singapore’s GDP exceeds $420 billion, powered by its finance, trade, and high-tech industries.
-
Malaysia: With a diversified economy, Malaysia’s GDP is approximately $400 billion, including electronics manufacturing and services sectors.chainup+1
Countries like Vietnam and the Philippines are rapidly climbing the economic ladder, fueled by manufacturing, technology, and remittances, with GDP figures around $450 billion and $410 billion, respectively.chainalysis
Economic Growth and Potential
Fastest Growing Economies in Southeast Asia
While the biggest economies dominate by size, emerging markets within Southeast Asia show remarkable growth potential:
-
Vietnam: Averaging 6-7% annual GDP growth, it is becoming a manufacturing hub attracting major foreign direct investments.
-
Philippines: Experienced rapid growth fueled by remittances, the services sector, and digital economy innovations.
-
Cambodia and Laos: Smaller economies growing fast due to improvements in infrastructure and expanding trade links.
This fast growth trajectory indicates shifting economic power within the region and rising middle-class consumers.chainup
Regional Economic Integration and Influence
ASEAN and Trade Cooperation
The Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) plays a critical role in boosting the region’s economic strength by fostering trade cooperation, reducing tariffs, and promoting investments among member countries. ASEAN’s combined GDP is now estimated at about $4.7 trillion, making it one of the world’s largest economic blocs by GDP.business.cornell+1
Singapore serves as a major financial hub linking Southeast Asia to global markets, while Indonesia’s vast market offers expansive opportunities. Malaysia and Thailand continue to serve as industrial and trade gateways in the region.
Challenges and Outlook
Addressing Economic Disparities and Sustainability
Despite robust growth, the region faces challenges like income inequality, infrastructure gaps, and environmental sustainability concerns. Southeast Asia’s economic future depends on improving education, digital infrastructure, sustainable development, and maintaining political stability to attract continued investment.business.cornell+1
Conclusion
Southeast Asia stands as one of the world’s most vibrant economic regions in 2025, with Indonesia leading as the largest economy followed by Thailand, Singapore, and Malaysia. Rapid growth in countries like Vietnam and the Philippines, combined with ASEAN’s regional integration efforts, enhances the region’s global economic stature. The future will hinge on addressing challenges and harnessing innovation to maintain this positive momentum.











8 comments
Ok think
Concise review article
Thanks for the information.
All right.
Thanks
Thanks to Indonesia, Asia overall will be in the direction growth potential except Myanmar
Thanks
Thanks for Knowledge 😀