Virtualization has revolutionized the way modern data centers operate by enabling better efficiency, scalability, and cost savings. Instead of running each application on a dedicated physical server, virtualization allows multiple virtual environments to run on a single physical machine. This technology has become a backbone for cloud computing, enterprise IT infrastructure, and large-scale data operations.
What is Virtualization in Data Centers?
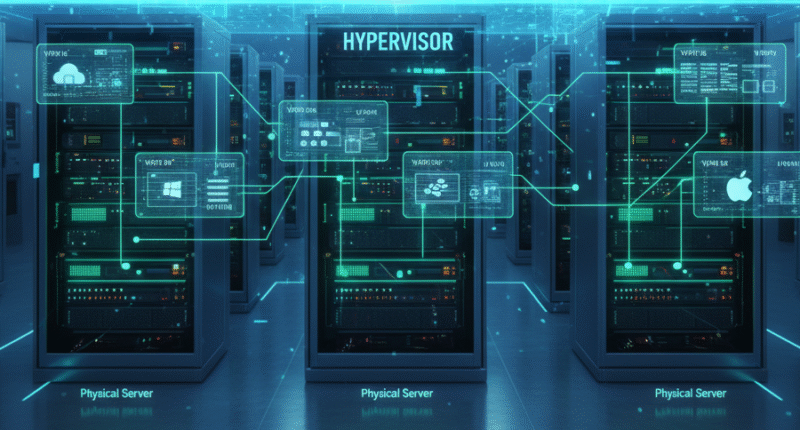
Virtualization is the process of creating a virtual version of hardware resources, such as servers, storage, and networks, using specialized software called a hypervisor. The hypervisor divides the physical server into multiple virtual machines (VMs), each running its own operating system and applications independently.
This approach enables businesses to utilize hardware resources more efficiently. Instead of dedicating an entire server to one application, multiple applications can share the same physical hardware without interfering with each other.
How Virtualization Works
Virtualization in data centers works through a combination of software and hardware integration. The key component is the hypervisor, which sits between the hardware and the virtual machines.
1. Role of the Hypervisor
A hypervisor is the software layer that manages and allocates resources such as CPU, memory, and storage to each virtual machine. There are two main types:
-
Type 1 (Bare-Metal Hypervisor): Runs directly on the server hardware and is typically used in enterprise data centers (e.g., VMware ESXi, Microsoft Hyper-V).
-
Type 2 (Hosted Hypervisor): Runs on top of an existing operating system and is more common for development and testing environments (e.g., VirtualBox, VMware Workstation).
2. Resource Pooling and Allocation
Virtualization pools computing resources and assigns them dynamically to workloads as needed. If one VM requires more memory or CPU power, the hypervisor can reallocate resources from other VMs without affecting performance.
3. Isolation and Security
Each virtual machine is isolated from others. If one VM crashes or is compromised, the other VMs on the same physical server remain unaffected, improving security and reliability.
Benefits of Virtualization in Data Centers
1. Improved Resource Utilization
Virtualization reduces underutilization of hardware, allowing data centers to maximize server usage and save costs.
2. Scalability and Flexibility
It becomes easier to deploy, clone, or migrate virtual machines, which helps businesses scale their infrastructure quickly.
3. Disaster Recovery and High Availability
VMs can be backed up and restored quickly, minimizing downtime in case of failures. Many data centers use live migration features to move workloads between servers without interruption.
Conclusion
Virtualization is the cornerstone of modern data centers, enabling efficient resource utilization, flexibility, and cost savings. By using hypervisors to create isolated virtual machines, organizations can consolidate workloads, improve security, and respond quickly to changing business needs. As technology advances, virtualization continues to evolve, paving the way for containerization and cloud-native infrastructure.









3 comments
Second time
The article refreshes memories of old time main-frame in data center, as discussion keeps going on virtualization through Hypervisor.
Really appreciate your efforts..